The difference between liquid pressure and air pressure
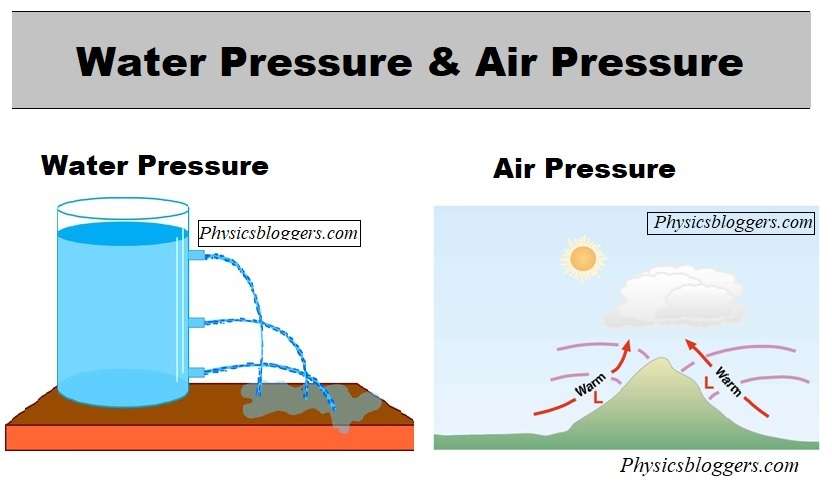
Water Pressure and Air Pressure
Introduction
Fluid tension and pneumatic force are two kinds of strain that can be experienced in various circumstances. The fundamental contrast between the two is the medium through which the strain is applied.
Fluid tension is the strain a fluid applies when it is very still. Not set in stone by the profundity and thickness of the fluid and is estimated in units, for example, pounds per square inch (psi) or pascals (Dad). The tension in a fluid is communicated consistently this way, implying that the strain at some random point in the fluid is similar in every way. This is because fluids are basically incompressible, implying that any power applied to a fluid will be communicated consistently through the liquid.

Pneumatic force, then again, is the strain applied by the climate on objects on the world’s surface. It is additionally estimated in units like psi or Dad. The strain of air shifts relies upon variables like height, temperature, and stickiness. Dissimilar to fluid strain, gaseous tension isn’t communicated consistently every which way. All things considered, it will in general diminish with height, and it can likewise be impacted by variables like breeze and choppiness.
The principal distinction between fluid strain and pneumatic stress is that fluid tension is the tension applied by a fluid and is sent consistently every which way, while gaseous tension is the tension applied by the environment and isn’t communicated consistently every which way.
Utilizations of Pneumatic stress and water pressure
Pneumatic stress and water pressure have different functional applications in our regular routines. Here are a few purposes of pneumatic stress and water pressure:
Utilizations of Gaseous tension:
Expansion:
Pneumatic stress is utilized for expanding tires, inflatables, pneumatic beds, and other inflatable items.
Pneumatic devices:
Gaseous tension drives pneumatic apparatuses like penetrates, mallets, and effect torques.
Shower painting:
Gaseous tension is utilized in splash painting to atomize the paint and create a fine fog, resulting in a smooth and even complexion.
Vacuum cleaners:
Pneumatic force is used in vacuum cleaners to pull and attract soil, flotsam, and jetsam.
Weather conditions gauging:
Gaseous tension is utilized to gauge air pressure, which assists in anticipating enduring examples and conditions.
Utilizations of Water Tension:
Water system:
Water pressure is utilized in water system frameworks to convey water to harvests and plants.
Firefighting:
Water pressure is utilized in firefighting to convey water through hoses to quench fires.
Hydroelectric power:
Water pressure is utilized to create power in hydroelectric power plants.
Pressure washing:
Water pressure is utilized in pressure washing to clean surfaces like structures, decks, and walkways.